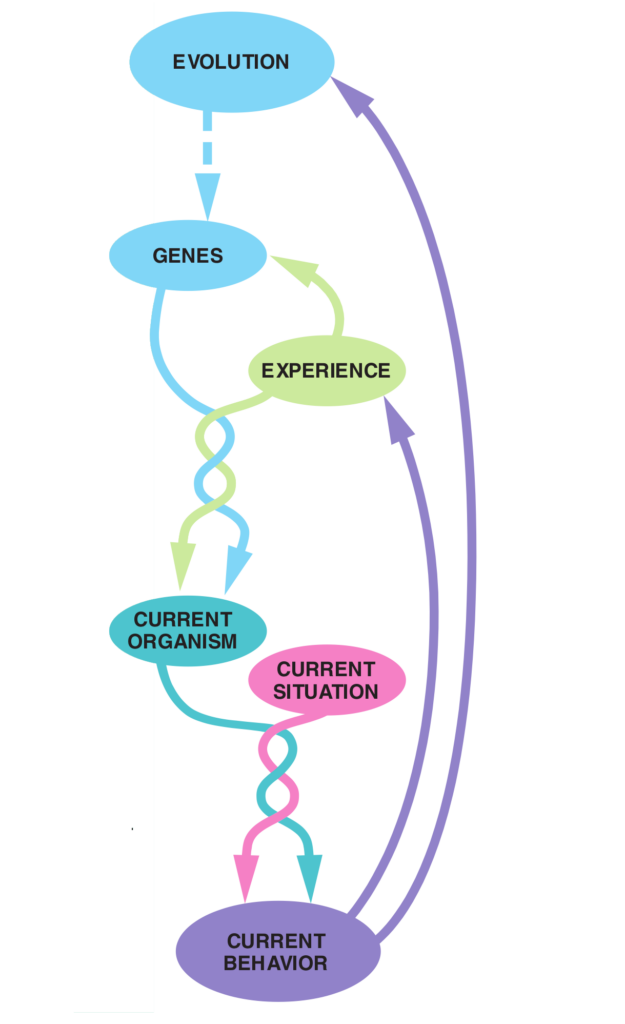
Selfish versus altruistic behavior
Selfish behavior is widely recognized as the behavior most rewarding for genetic evolutionary fitness. The EACH project however, finds that altruistic behavior under the right circumstances can be beneficial for the survival of species over selfish beahvior. To show this, consider two types of asexual individuals exist in the population, differing only in their altruistic…